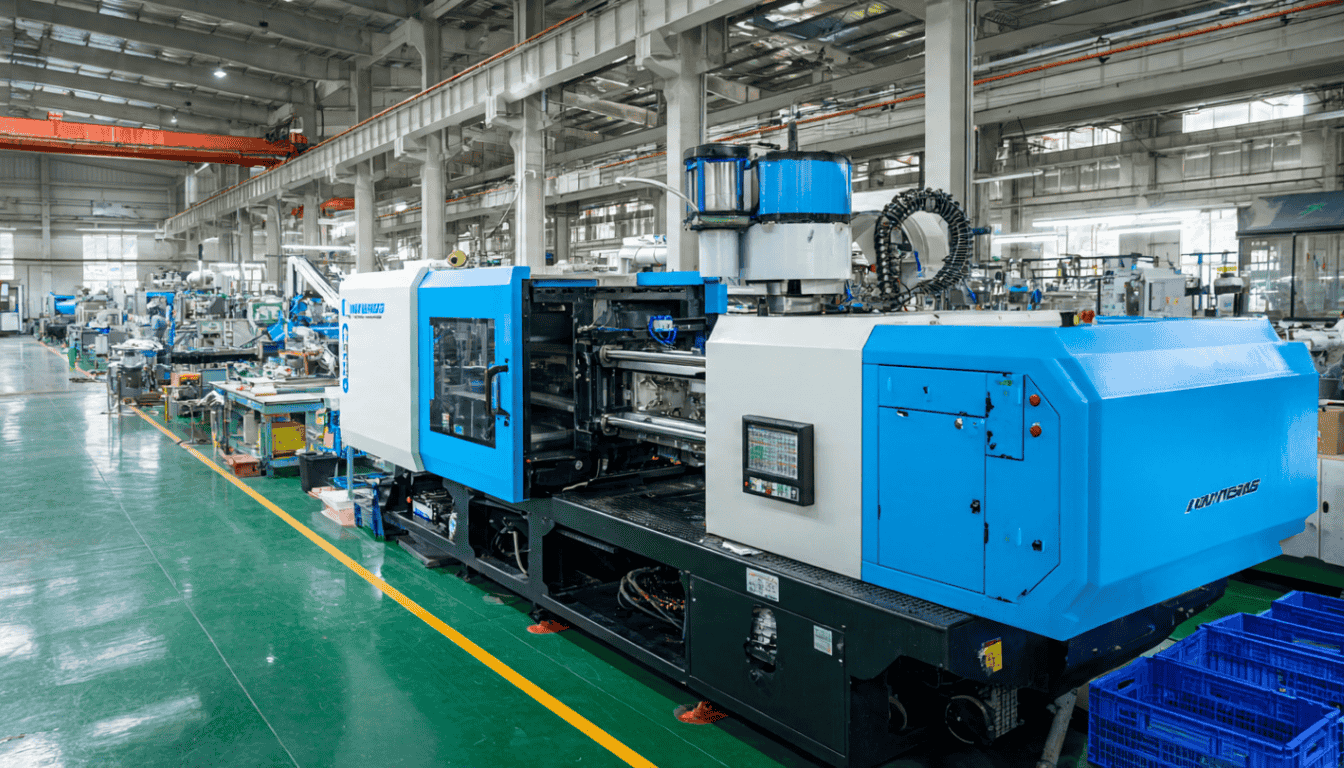
Plastic injection molding is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes in modern industry.
Plastics are commonly applied in automotive components, home appliances, and electronic products. These plastic components are typically required to be produced in high volumes while maintaining consistent quality.
For global OEMs, plastic injection molding is not merely a production method, but a strategic solution within the modern manufacturing supply chain.
The Role of Plastic Injection Molding in Modern Industrial Production
In today’s global manufacturing environment, industries demand components with high accuracy, durability, cost efficiency, and consistent quality.
Plastic injection molding addresses these requirements by integrating advanced machinery, precision mold design, and appropriate plastic material selection.
As global supply chains continue to become more integrated, plastic injection molding has become a critical process to support mass production while meeting high-quality and international manufacturing standards.
What Is Plastic Injection Molding?
Plastic injection molding is a manufacturing process in which molten plastic material is injected into a closed mold under high pressure.
Once the material cools and solidifies, the plastic product is ejected from the mold according to the shape and dimensions defined by the mold design.
The term injected plastic refers to thermoplastic material that has been melted and injected into the mold.
This process enables the production of components with complex geometries, tight tolerances, and consistent results in large quantities, making it highly suitable for industrial and OEM applications.
How Does the Plastic Injection Molding Process Work?
For engineers, purchasing teams, and decision makers in manufacturing industries that utilize plastic components, understanding the plastic injection molding process is essential.
The plastic injection molding process consists of several key stages, each of which must be precisely controlled to ensure product quality.
Stages of the Plastic Injection Molding Process
1. Plastic Material and Mold Selection
The process begins with selecting the appropriate plastic material based on product requirements, including mechanical strength, heat resistance, dimensional stability, and cost considerations.
At the same time, the mold must be properly prepared and designed according to the product geometry, including the core, cavity, runner system, gate design, and cooling channels. Errors in mold design can directly impact the final product quality.
2. Material Feeding
The selected plastic material is fed into the injection molding machine through a hopper.
The plastic pellets are then conveyed into the barrel for further processing. At this stage, material cleanliness and pellet size consistency are critical, as they significantly affect process stability and molding quality.
3. Melting and Injection
Inside the barrel, the plastic material is heated until it reaches its melting temperature based on its material characteristics.
The screw within the injection unit pushes the molten plastic forward and injects it into the mold under high pressure.
Injection pressure and speed are precisely controlled to ensure uniform flow and complete filling of the mold cavity according to the product design.
4. Mold Filling and Holding Pressure
Once the mold is fully filled, holding pressure is maintained for a specific period. This stage compensates for material shrinkage during cooling and ensures accurate dimensions while preventing defects such as sink marks or voids.
5. Cooling and Solidification
The injected plastic is cooled through the cooling system built into the mold. Uniform cooling is essential to maintain dimensional stability and prevent part deformation. Cooling time is adjusted according to the plastic material type and part thickness.
6. Ejection and Inspection
After the part has fully solidified, the mold opens and the ejector system pushes the product out of the mold.
The part is then inspected to ensure there are no visual defects, dimensions meet specifications, and surface quality complies with required standards before proceeding to the next process or packaging.
A well-controlled plastic injection molding process allows manufacturers to achieve high dimensional accuracy, consistent surface quality, and optimal production efficiency, especially for mass production and OEM applications.
What Types of Plastics Are Used in Injection Molding?
Plastics used in injection molding are generally classified into two main categories: commodity plastics and engineering plastics.
This classification helps manufacturers and OEMs determine the most suitable material based on application requirements, expected mechanical performance, environmental resistance, and production cost considerations.
Selecting the right plastic material significantly influences product functionality, service life, surface appearance, and overall manufacturing efficiency.
Commodity Plastics in Injection Molding
Commodity plastics are the most commonly used materials in injection molding, particularly for high-volume production with standard performance requirements.
These materials are selected due to their ease of processing, wide availability, and relatively low cost.
Common types of commodity plastics include:
1. Polypropylene (PP)
PP is lightweight, chemically resistant, and offers good flexibility. It also provides excellent fatigue resistance, making it suitable for components requiring repeated bending, such as housings, covers, and interior parts.
2. Polyethylene (PE)
PE is available in several grades, including HDPE and LDPE. HDPE offers higher strength and stiffness, while LDPE provides greater flexibility. PE is widely used for components requiring impact resistance and moisture resistance.
3. Polystyrene (PS)
PS is rigid, dimensionally stable, and easy to process. It is commonly used in consumer products with simple shapes and specific aesthetic requirements.
4. Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC)
PVC is known for its good chemical resistance and can be formulated as either rigid or flexible material. It is used in various non-structural applications and components requiring insulation properties.
Commodity plastics are widely applied in home appliance components, consumer products, packaging, and non-structural parts that do not require high mechanical loads.
Engineering Plastics in Injection Molding
Engineering plastics are used for applications that require higher performance compared to commodity plastics.
These materials are designed to offer superior mechanical strength, higher heat resistance, and improved dimensional stability, making them suitable for industrial and OEM applications.
Common engineering plastics used in injection molding include:
1. Polycarbonate (PC)
PC offers excellent impact resistance and good thermal stability. It also provides high optical clarity, making it suitable for transparent or semi-transparent components. Typical applications include electronic components, automotive lighting parts, and protective covers.
2. Polymethyl Methacrylate (PMMA)
PMMA is known for its outstanding optical transparency and glossy surface finish. It also has good weather resistance, making it suitable for outdoor applications such as lamp covers, display panels, and visually critical components.
3. Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
PBT provides excellent dimensional stability, heat resistance, and electrical insulation properties. It is commonly used in automotive and electronic components such as connectors, housings, and parts exposed to temperature and humidity variations.
4. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS)
ABS combines good mechanical strength, toughness, and surface quality. It is easy to process and widely used in automotive interiors, electronic housings, and consumer products requiring high aesthetic standards.
5. PP Compound
PP compound is modified polypropylene reinforced with fillers or additives such as glass fiber, talc, or minerals.
These modifications improve stiffness, strength, and dimensional stability compared to standard PP. PP compounds are commonly used in lightweight structural automotive components and housings that require balanced performance and cost efficiency.
6. Polyamide (PA / Nylon)
PA offers high mechanical strength, excellent wear resistance, and good thermal stability.
Certain grades also provide self-lubricating properties. PA is widely used for gears, brackets, and automotive components subjected to mechanical loads and friction.
7. Polyoxymethylene (POM)
POM is known for its low friction, high stiffness, and excellent dimensional stability. It is ideal for precision components such as gears, snap-fit parts, and locking mechanisms requiring tight tolerances and smooth movement.
8. Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA)
ASA has similar properties to ABS but offers superior resistance to weathering and UV exposure.
It is commonly used for outdoor applications and automotive exterior components that require durability without compromising surface appearance.
Engineering plastics are widely applied in automotive components, electronic parts, and precision industrial products that require long-term reliability and performance.
How to Choose the Right Plastic Material
Material selection should consider mechanical strength, heat resistance, chemical resistance, dimensional stability, and the balance between performance and cost.
Experienced injection molding manufacturers typically provide engineering support to ensure the selected material meets application requirements and industry standards.
Injection Molding Parts and Mold Components
Injection molded parts are produced using precision-engineered molds. Key mold components include the core and cavity, runner and gate systems, cooling channels, and ejector mechanisms.
Proper mold design significantly affects product quality, cycle time, and production efficiency.
Why Plastic Injection Molding Is Essential for OEMs
For OEMs in automotive, electronics, and home appliance industries, plastic injection molding offers high precision, consistent quality, design flexibility, and cost efficiency for large-volume production.
The process supports global manufacturing strategies by delivering stable and repeatable production results.
Banshu Plastic: A Professional Plastic Injection Manufacturing Partner for Global Markets
Banshu Plastic Indonesia is a professional plastic injection manufacturing company serving OEMs and global industries. With over 20 years of experience, we have become a trusted partner for customers in the automotive sector, particularly in plastic injection molding.
As an active member of IMDIA (Indonesia Mold & Dies Industry Association), Banshu Plastic is closely connected to the national ecosystem of mold and dies manufacturing, enabling us to stay aligned with industry best practices, technological developments, and quality standards.
Our technical expertise is reinforced by the implementation of international quality standards and premium certifications, including IATF 16949:2016, ISO 14001:2015, and ISO 9001:2015.
These certifications reflect our commitment to product quality, process consistency, and environmental responsibility across all manufacturing activities.
Built on this strong foundation, Banshu Plastic supports industries with high-quality plastic components for automotive, electronics, and home appliance applications.
Every project is managed through a mature engineering approach, with a strong focus on each customer’s specific technical and production requirements.
Supported by strict quality control systems and manufacturing readiness aligned with international standards, Banshu Plastic is committed to growing together with our customers as a reliable long-term partner in plastic injection molding solutions.
Click Get Quote to connect with our team and discuss how Banshu Plastic can support your production requirements.